What is Blockchain? | Blockchain Technology Explained

What is blockchain?
Blockchain is the technology behind cryptocurrencies. If you are into cryptocurrency then along with bitcoin I am sure you must have heard of Blockchain.
Blockchain is a database but it’s quite different from the regular database. To understand it more clearly first we have to understand what is a database.
What is a database?

A database is a collection of data stored on a computer system in an electronic format. Information in a database is stored in an organised manner which makes it easier to access information from it.
We can take an example of a spreadsheet. In a spreadsheet, we store data in columns and rows and make it organise so that whenever we need to access the data we can easily do that. But spreadsheets are useful for a small amount of data. Databases are designed to store a large amount of data.
Databases are also called servers which are made of powerful computers to store a high amount of data. These servers require a bigger space like a warehouse. Spreadsheets are usually owned by a single individual or a group of people while databases are owned by businesses or big organizations that have a high amount of data to store.
Now, here the method of storing data in the blockchain is different. Information stored in the blockchain is stored in the form of blocks. Blocks are basically groups of information. Blocks have a limited storage capacity and when one block is filled it is chained to the previous block forming a chain and this is known as a blockchain.
Data stored in blockchain are irreversible which means information once stored cannot be changed. Now we will learn the reason behind it later in the article.
Who founded blockchain technology?
In 1991 Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta, two researchers gave an outline of blockchain technology where they wanted a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with.
Blockchain technology gained its popularity when Satoshi Nakamoto released the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008 where he explained blockchain technology.
People got to know about the technology behind bitcoin and blockchain became popular around the world. New cryptocurrencies were created using blockchain.
How does transaction happen in blockchain?
To understand blockchain, we have to take a real-life example. You are playing cricket along with your other three friends. Now while playing you realize you don’t have anyone to count your scores. So, one of your friends suggested that he is going to get one person who would count their scores and wickets in the match. But then you realise that you cannot trust the other person and he/she may manipulate the scores. So, you come up with an idea that all the players would keep a piece of paper with them and each one would update the score after every ball when the game will be overall would compare the 4 pieces of paper and then decide who won the match. If someone manipulates the score, it would not change on the other 3 papers and in this way no one can cheat.
Similarly, this is the way in which blockchain works. There are a lot of computers that are connected peer-to-peer. They are known as nodes. Today there are over 47000 nodes all around the world.
In the case of cryptocurrency, all of the computers maintain a ledger that has records of all the transactions that have happened. Whenever any transaction happens it is shared with the nodes and the transaction gets recorded in every copy of the ledger of all the nodes around the world.
When a new transaction occurs, it is shared with all the nodes around the world through a peer-to-peer connection. Then all the nodes solve mathematical equations to validate the transaction. After a transaction is validated, then the information is converted into a block and once a block is filled it is added to the chain.
Is Blockchain Secure?
Yes, blockchain is really secure and it is very difficult for hackers to take information from the blockchain. Let me explain this process by showing you how is data stored in blocks and why it cannot be accessed by hackers.
As we know blockchain stores data in the form of blocks.
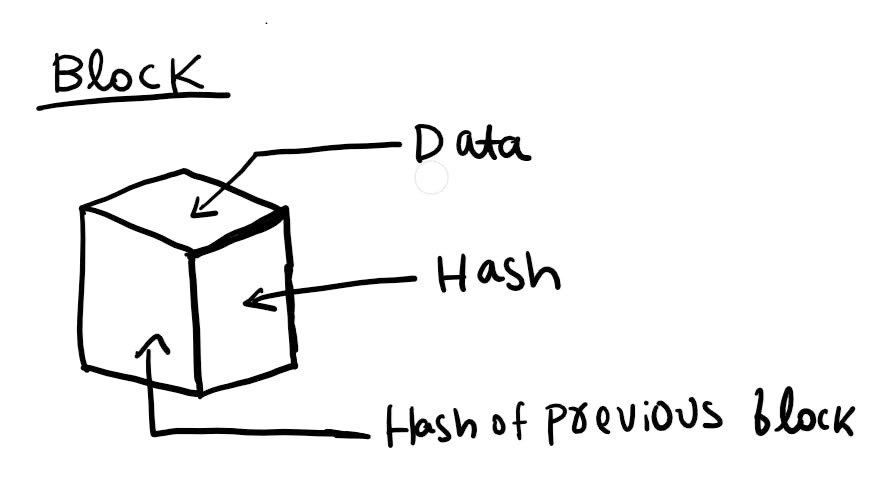
In the above image, we can see this is how a block is structured in the blockchain. In a block there are three parts, first is data, second is hash and third is the hash of the previous block. Now let us discuss them in detail.
Data – Here the details of the transaction are stored, like the name of the sender, receiver, amount of bitcoin, etc.
Hash – This is a unique feature of the blockchain. Each block contains a unique hash code which is a combination of letters and numbers.
Hash of the previous block – The block contains the hash code of the previous block as well. But the very first block in the chain does not have a previous block. So that block is known as a genesis block.
Now let us go ahead and see what happens when someone tries to make changes to any block.
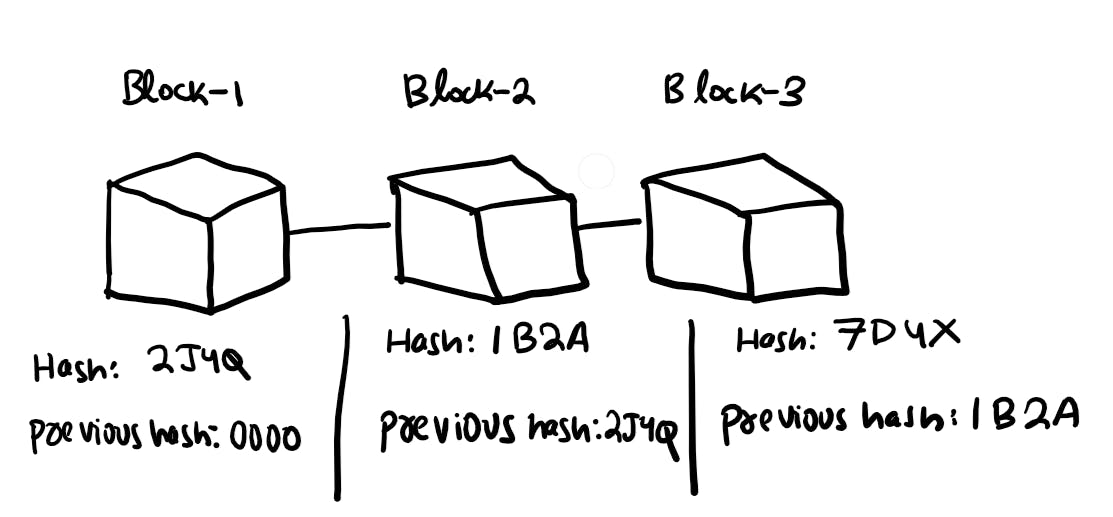
As you can see in the above image this is the way in which blocks are arranged in the blockchain. Block-1 is linked to Block-2, similarly, Block-2 is linked to Block-3 and this continues.
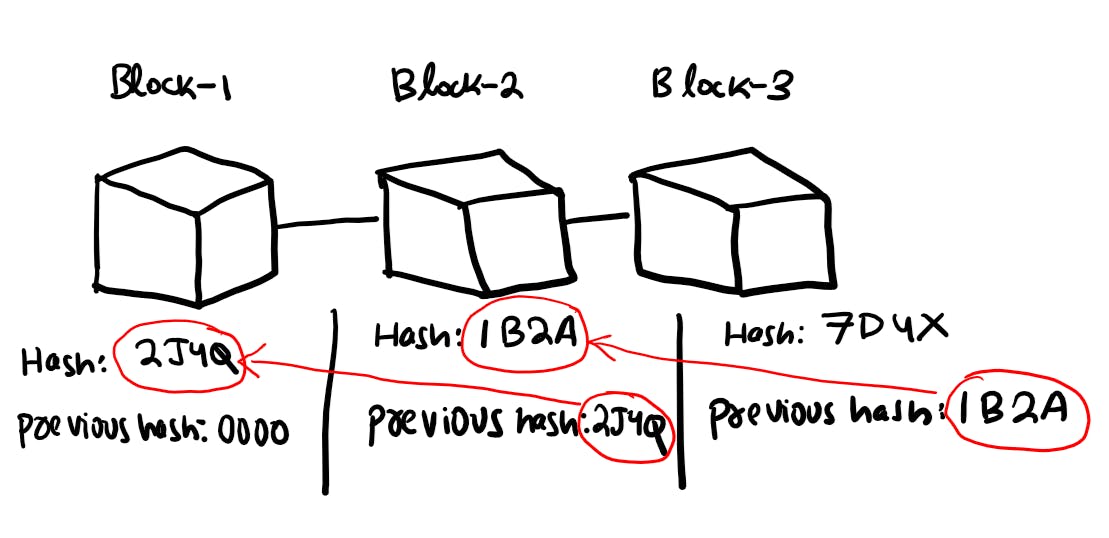
Now as I have told you that each block contains the previous hash of the previous block. This is what makes the transaction a lot more secure. Whenever you make some changes to any block, the hash code of the block changes.
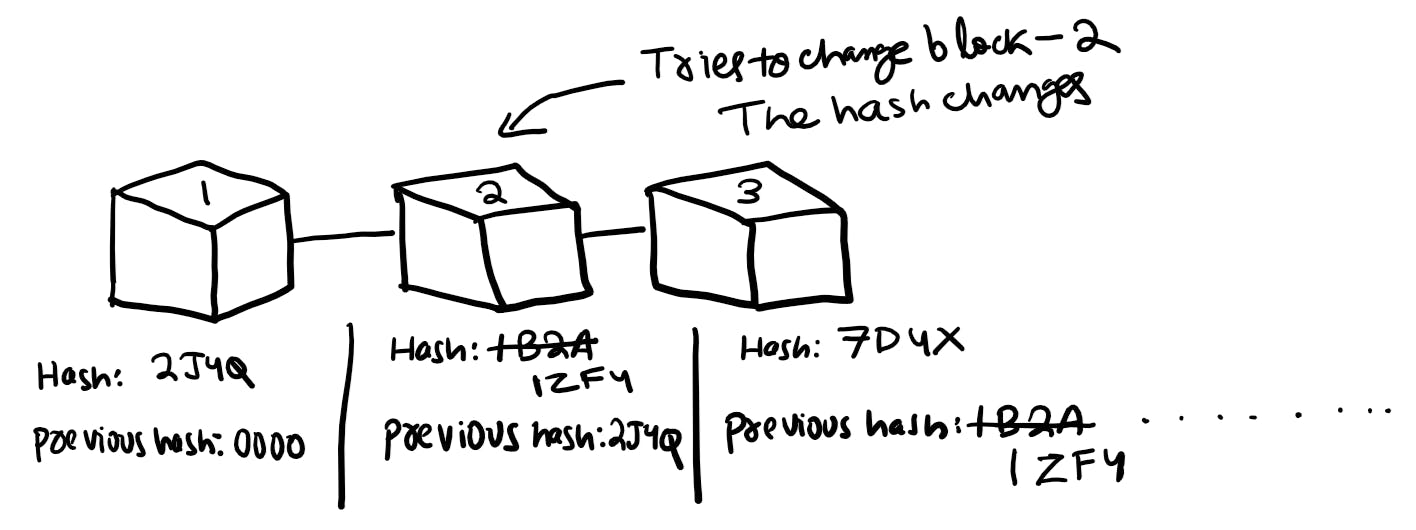
Suppose any hacker tries to access Block-2 then, the hash code of the block would change and then when the hash code of the block would change, the next block containing the hash code of this current block would not match and hence all the following blocks would become invalid and here the chain would break. In this way, the hacker cannot extract information from any block.
But still, this is not enough as today computers are really powerful and they could calculate 1000s of hashes in minutes. So, even if the chain breaks one could easily calculate all the hashes and again build the chain. So, to prevent this blockchain uses a technology called proof-of-work. It slows down the formation of a new block by 10 minutes. So whenever the chain breaks, to create a new block there is a delay of 10 minutes which makes it very hard to build the blockchain again.
Now, the best part is that since this is decentralized, so when a blockchain breaks no one has to depend upon a single entity to fix the blockchain, any node from around the world can do that.
Blockchain is decentralized
You must have heard that all cryptocurrencies are decentralized, e.g. bitcoin, which means that there is no particular person or organization owning it. This is because the technology blockchain is decentralized.
Uses of Blockchain
Today majority of the blockchain technology is used for cryptocurrencies, but blockchain can be used for other things as well.
Supply Chains
Today many supply chain companies like De Beers, Unilever, etc. are using blockchain in their supply chain. IBM has created a Food Trust blockchain to track the food product's journey since a lot of hazardous materials are introduced to food items. Blockchain was used to find out where these hazardous materials come from.
Banking and Financial Sector
One sector for which Blockchain technology is very ideal is the Banking and Financial Sector. When you deposit a cheque in a bank, it takes some time to process the money into your account. To save time and secure transactions, blockchain technology could be used.
Banks only work during business hours and on working days. But Blockchain never sleeps. The transactions can be processed 24×7, which will result in faster transactions and saving time. So, a lot of transactions can happen in less time.
Healthcare Sector
In the Healthcare sector blockchain has a vital role. Medical records can be stored on the blockchain network. Physical medical records have a high risk of getting changed, stolen or destroyed. But on the blockchain network, the records will be in digital form and will stay safe.
Conclusion
So, I hope you have understood what is blockchain and how it is so useful for every sector. If you have any doubts then feel free to ask them in the comments and I will reply to them. Thanks for reading 🙂
 Aniket Bindhani Blog
Aniket Bindhani Blog